Measles, chickenpox, scarlet fever, and rubella are some examples of common childhood illnesses with rashes, which are caused by viruses and bacteria and are transmitted through the hands and in the air, such as with sneezing and cough.
You will need to see a doctor, since many childhood illnesses are very contagious. Nowadays, children can be immunized with a trivalent vaccine against measles, mumps, rubella and chickenpox (MMR and chickenpox).
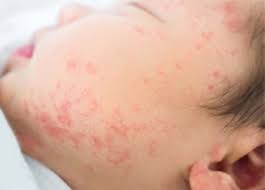
Rashes occur in babies and children, caused by allergies or an invasion of mites.
SUMMARY OF THE MOST IMPORTANT CHILDHOOD ILLNESSES WITH RASH
1 Three-day fever
Three-day fever is more common in babies between six and 12 months old. For three days, the child has a high fever, around 40ºC, even if afterwards the temperature drops rapidly. When the child has no fever, an irregular, pale red rash often appears on the face and trunk and begins to go away after two days.
Three-day fever is spread by coughing and touching. The contagion phase goes away when the rash first appears. The incubation period, which is the time interval between contagion and the onset of the disease, lasts between five and 15 days.
2 Measles
Measles is a viral illness that usually manifests with flu-like symptoms, such as fever, cough, and cold. The typical rash with pale red patches presents about four days later and can be extremely itchy. This rash appears first on the face and behind the ears and later spreads to the trunk and legs.
When catching measles, children often cough a lot and have a high fever that can reach 40ºC. During illness, they are very weak and become sensitive to light, therefore they require absolute rest. The fever and rash start to go away in about four days.
Measles is an extremely contagious viral disease, the pathogens of which are transmitted by droplets dispersed in the air. Thanks to vaccination, measles has become a relatively rare disease in people. The incubation period is one to three weeks.
3 Fifth disease
Fifth disease is characterized by a red lenticular rash that appears on the face and can spread all over the body. In some cases there are so many spots that they converge into circles. Pathogens are viruses transmitted by droplets in the air.
Colds, low fever, and headaches and throat aches can be symptoms of the disease, and the rash does not appear for ten days. After about a week, the rash will start to go away. Fifth disease is usually mild in children, so there is no need for treatment. However, it can be dangerous in pregnant women. The incubation period lasts two to three weeks.
4 Rubella
Rubella is a viral disease that appears in children as inflammation of the lymph nodes behind the ears. A day or two after a pale red rash appears, it normally starts on the back of the ears and spreads all over the body.
The rash usually presents with fever and painful inflammation of the lymph nodes in the throat. It is a mild illness in children and the spots get smaller one to three days later. The MMR vaccine protects many children against rubella.
Notwithstanding, rubella is dangerous for pregnant women, as it can cause serious malformations of the fetus during the first three months of pregnancy. The incubation period is between two and three weeks.
5 Scarlet fever
Scarlet fever is a childhood disease that is characterized mainly by the famous "strawberry or raspberry tongue" and usually appears in children between three and eight years old. At first the tongue is white, but after a few days it becomes red and swollen.
In addition, many children have bad breath. Scarlet fever normally manifests with fever, difficulty swallowing, and a severe sore throat. For the next two days, children may have the typical rash as dense spots, like needle heads, that extend all over the body from the armpits and groins.
The disease resolves between two and six days later. Sage tea and neck compresses help relieve sore throat. Scarlet fever is a disease caused by streptococcal bacteria that are spread through droplets in the air or through contact with contaminated objects or surfaces. The incubation period lasts two to four days.
As a rule, scarlet fever in children is treated with penicillin. This can prevent complications like otitis media or pus on the tonsils. In addition, administration of penicillin reduces the risk of infection to one day, while without it children can be contagious for up to two weeks.
6 Varicella
Chickenpox is a very common disease caused by a virus that is usually spread through coughing and sneezing. In addition, viruses can cause infections even at great distances.
About two weeks after the infection, the child feels weak and has a fever. Chickenpox in children can develop at different intensities. Often itchy blisters form and appear on the face and then spread to the chest, arms and legs.
The blisters can also infect the mucous membranes of the eyes, mouth, pharynx, and genitals. The rash goes away a week or two later. Children should avoid scratching so that the blisters are not irritated and scars do not remain.
To relieve the itching you can apply a manzanilla dilution or zinc ointment on the blisters. The trivalent vaccine protects babies against chickenpox.
7 Human foot-and-mouth disease
Human foot-and-mouth disease produces reddish spots on the mouth, palms of the hand, and the soles of the feet. The rash is not itchy and goes away after ten days, but the condition is very uncomfortable, since painful blisters can appear in the mouth.
Cold, liquid foods such as yogurt and porridge are very good for children. However, you should avoid acidic foods, as they irritate the affected oral mucosa. This disease can cause fever, stomach pain, and vomiting.
Human foot-and-mouth disease is a viral infection that is transmitted through the air and is particularly caught in recreation centers and nurseries. The incubation period lasts about three to six days.


0 Comments